A national study finds major variations in hearing aid use by race, income and education — but VA insurance coverage levels the playing field.
5:15 PM
Author |
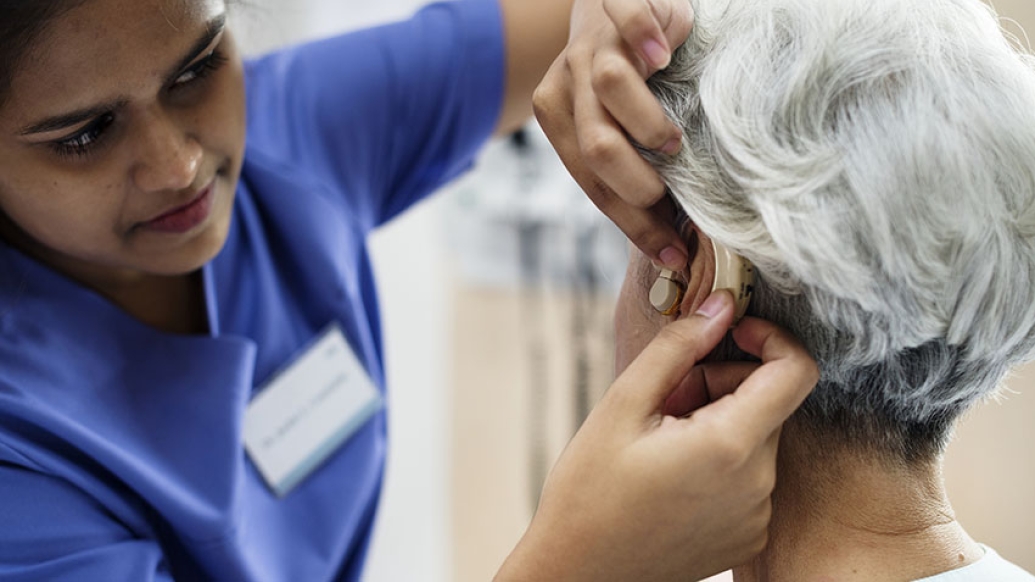
Hearing loss seems like one of the great equalizers of old age, striking people of all kinds as their ears gradually lose the ability to pick out sounds or hear certain pitches.
LISTEN UP: Add the new Michigan Medicine News Break to your Alexa-enabled device, or subscribe to our daily audio updates on iTunes, Google Play and Stitcher.
But a new national study reveals major gaps in whether Americans over age 55 get help for their hearing loss — gaps that vary greatly by age, race, education and income.
In all, just over a third of older adults who say they have hearing loss are using a hearing aid to correct it, the study finds. But those who are non-Hispanic white, college educated or have incomes in the top 25 percent were about twice as likely as those of other races, education levels or income ranges to have a hearing aid.
The cost of hearing aids is most to blame, say the researchers from the University of Michigan who published the study in The Gerontologist. They presented it this week at the annual research meeting of the AcademyHealth professional society for health care researchers.
Hearing aids can cost thousands of dollars out of a patient's pocket because most health insurance programs, including Medicare, don't cover them.
In fact, the study finds that the only factor that leveled the playing field for hearing aid use was having insurance through the Department of Veterans Affairs, which covers hearing aids in many cases. Hearing-impaired veterans ages 55 to 64 were more than twice as likely as their nonveteran peers to use a hearing aid, even after the researchers corrected for other differences. The gap between veterans and nonveterans was also significant for those over 65.
But the detailed interviews conducted for the study also show that personal concerns about hearing aid use, and lack of engagement with health providers, play a role.
"Hearing aids are not easy for many to obtain due to their costs," says Michael McKee, M.D., MPH, the U-M family medicine physician and assistant professor who led the analysis.
"However, there are a number of additional issues that place at-risk groups at an even larger disadvantage to achieving good hearing health. Many of these issues are beyond the financial aspects, including racial/ethnicity and sociocultural elements, for instance stigma and vanity."
[T]here are a number of additional issues that place at-risk groups at an even larger disadvantage to achieving good hearing health.Michael McKee, M.D., MPH
National survey and local interviews
McKee, who uses a cochlear implant to overcome his own hearing loss, worked on the study with Helen Levy, Ph.D., a health economist and professor at the U-M Institute for Social Research, and other colleagues. The authors are members of the U-M Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation.
MORE FROM THE LAB: Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
They used survey data from the nationally representative Health and Retirement Study, which is based on interviews conducted by the Institute for Social Research with funding from the National Institutes of Health.
The analysis included data from more than 35,500 people nationwide over age 55 who said they had hearing loss. In addition, McKee and colleagues conducted in-depth interviews with 21 other older adults with hearing loss in the communities surrounding the university.
The authors conclude that the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services should consider covering hearing aids for Medicare participants and those in Medicaid plans for lower-income adults of any age. Some state Medicaid plans do cover hearing aids, but it is not required.
"Many people may not realize that Medicare does not cover hearing aids," says Levy. "But it doesn't, so cost can be a significant obstacle preventing older adults with hearing loss from getting the help that they need."
More findings from the study:
-
The percentage of older adults with hearing loss who used a hearing aid rose with age, from about 15 percent of those in their late 50s to more than 57 percent of those in their late 80s.
-
Forty percent of non-Hispanic white adults with hearing loss used a hearing aid, compared with 18.4 percent of non-Hispanic black and 21.1 percent of Hispanic adults with hearing loss.
-
Nearly 46 percent of hearing-impaired older adults who had gone to college reported that they used a hearing aid, compared with just under 29 percent of those who hadn't graduated from high school.
-
Nearly half of those with incomes in the top 25 percent wore a hearing aid, compared with about one-quarter of those in the bottom 25 percent.
-
There were no significant differences in hearing aid use based on the size of the community where the person lived, nor their level of health literacy as measured on a standard test.
-
Interviews showed that cost, lack of insurance coverage (or knowledge about insurance coverage), vanity and stigma were common reasons for not using hearing aids. Participants also cited a lack of attention to hearing loss by their primary care provider and worries about finding an audiologist they could trust.
-
Many interview participants who used a hearing aid mentioned efforts that hearing-related professionals made to connect them to discounts and insurance programs.
More about hearing loss
Estimates of hearing loss incidence place it at 29 percent of people in their 50s, 45 percent of those in their 60s, 68 percent of those in their 70s and 89 percent of those in their 80s.
Previous studies have shown that untreated hearing loss reduces older adults' ability to carry out everyday tasks, reduces their quality of life and is linked to social isolation, lower income, reduced cognitive function and poorer physical and psychological health.
A recent study led by McKee's colleague Elham Mahmoudi, Ph.D., found that having a hearing aid was associated with a lower chance of being hospitalized or visiting an emergency room in the past year. That study focused on people over 65 who had severe hearing loss, and it used data from a federal database.
McKee leads the Health Info Lab, which is researching health information use and literacy among deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals.

Explore a variety of healthcare news & stories by visiting the Health Lab home page for more articles.

Department of Communication at Michigan Medicine
Want top health & research news weekly? Sign up for Health Lab’s newsletters today!





